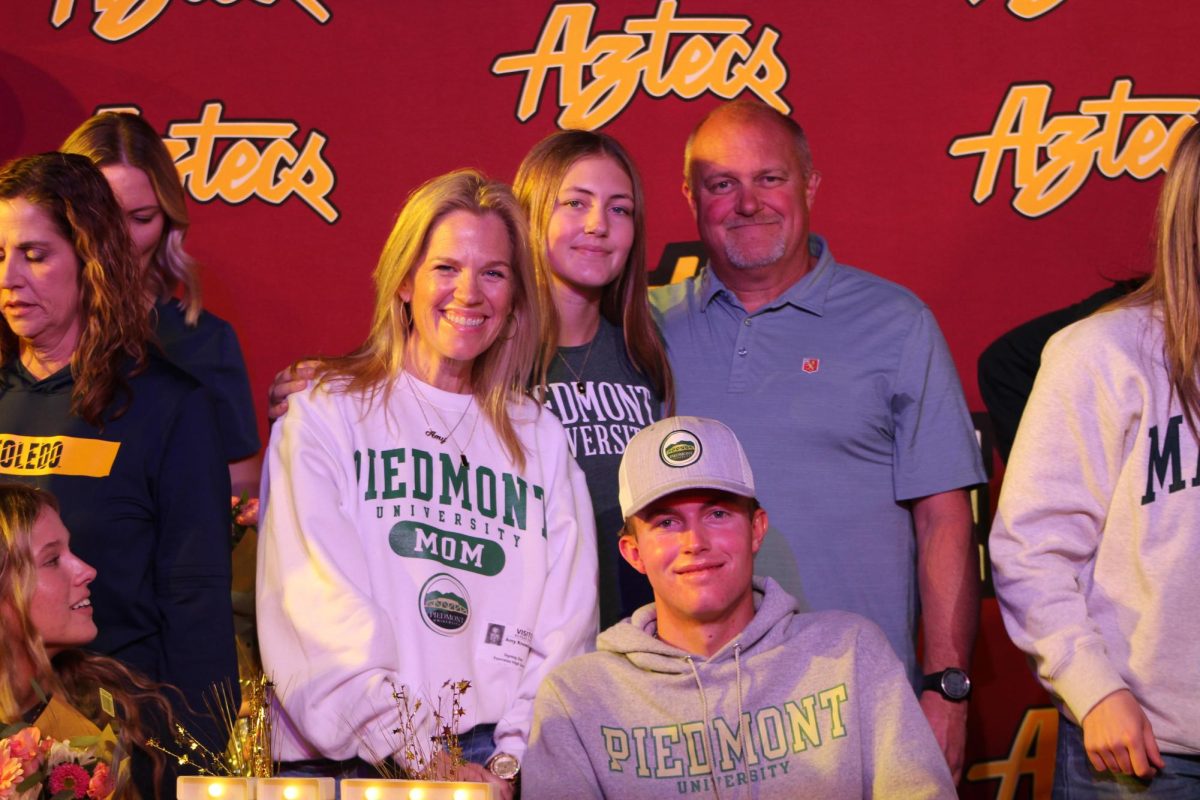
Boycotting of The 2022 Olympics Explained
May 23, 2022

The 2022 Winter Olympics were held in Beijing, China, from February 4 to February 20, 2022. These games were attended by 84 countries, although many people urged for a boycott, whether it was to refuse to watch or participate. In response to China’s human rights record, Canada, Australia, the United Kingdom, and the United States launched a diplomatic boycott of the 2022 Winter Olympics. These nations’ athletes competed, but no government officials were in Beijing. China had warned the four boycotting countries that their actions were a mistake, and that there would be a price to pay.
Why did these nations boycott? Why did people urge for boycotts? Jen Psaki, press secretary for the White House, noted “…ongoing genocide and crimes against humanity in Xinjiang and other human rights abuses,” and stated that while they “will not be contributing to the fanfare of the Games,” Team USA has their full support. Earlier this year, the United States concluded that China’s treatment of Uyghurs qualified as genocide and crimes against humanity, including the use of internment camps, forced labor and sterilization. The Uyghurs are a Muslim minority population that live in the northwestern area of Xinjiang, and have been targeted by the Chinese government. They have been detained and sent to concentration camps to be brainwashed and coerced to reject their religion. The major purpose is to eliminate their ethnic and cultural backgrounds in order to “make them Chinese” and pledge allegiance to the Chinese Communist Party. To further eliminate their identity, officials force them to eat pork and drink alcohol, and Uyghur women are married off to Chinese men.
In a statement issued by the Chinese Mission to the United Nations, China countered fiercely, accusing the US of measures that “politicize sports, create divisions, and instigate confrontation.” Nonetheless, despite their sentiment that politics should be kept out of sports, China has a history of issuing boycotts motivated by politics. From 1952 through 1980, China boycotted the Summer Olympics due to concerns about Taiwan’s participation. Over a missile defense debate, it limited tourists to South Korea’s 2018 Pyeongchang Winter Olympics. It sanctioned the NBA Houston Rockets in 2019 when one of its employees tweeted in support of Hong Kong’s democracy movements.